[Solved]write the full code in visual basic 2015 and steps Q37218950
Please write the full code in visual basic 2015 andsteps

Expert Answer
Answer to Please write the full code in visual basic 2015 and steps… . . .
[Solved]Rewrite System Matrix Format Find Augmented Matrix Reduce Augmented Matrix Reduced Row Ec Q37176743
a. Rewrite the system in matrix format, find the augmentedmatrix and reduce the augmented matrix to reduced row echelon form(rref) using Gauss-Jordan Elimination to determine the solution ofthe system (Solve it without using MATLAB please)
b. Check your answer of part (a) using the rref function in MATLAB.Write out the code (all the code) you typed into the CommandWindow.
c. Show that matrix A is singular by obtaining −1 using rowreduction to reduce [ | ]reduced row echelon form (rref) to showthat A can never be reduced to I. Write down the warning that youget in MATLAB when using the inv function to find the inverse.
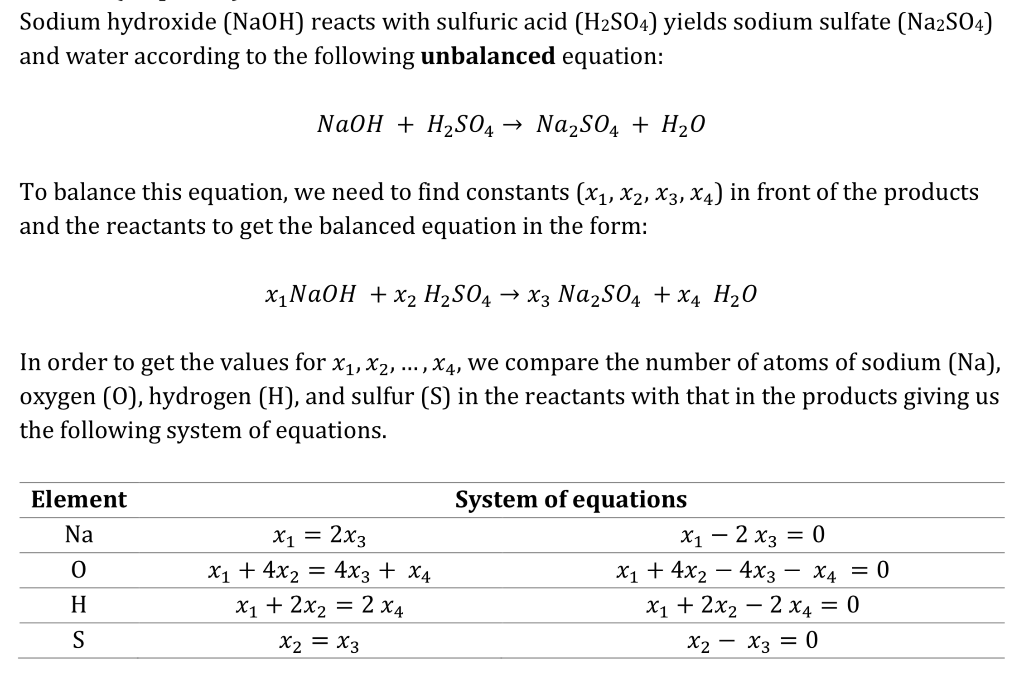
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) reacts with sulfuric acid (H2S04) yields sodium sulfate (Na2S04) and water according to the following unbalanced equation: NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O To balance this equation, we need to find constants (x1, x2, xa, xa) in front of the products and the reactants to get the balanced equation in the form: In order to get the values for x1,x2, …, x4, we compare the number of atoms of sodium (Na), oxygen (O), hydrogen (H), and sulfur (S) in the reactants with that in the products giving us the following system of equations. Element System of equations 0 x, + 4×2 4×3 + x4 x, + 4×2-4×3-X4-0 x1 + 2×2-2×4 x1 + 2×2 -2×40 3 2 3 Show transcribed image text Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) reacts with sulfuric acid (H2S04) yields sodium sulfate (Na2S04) and water according to the following unbalanced equation: NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O To balance this equation, we need to find constants (x1, x2, xa, xa) in front of the products and the reactants to get the balanced equation in the form: In order to get the values for x1,x2, …, x4, we compare the number of atoms of sodium (Na), oxygen (O), hydrogen (H), and sulfur (S) in the reactants with that in the products giving us the following system of equations. Element System of equations 0 x, + 4×2 4×3 + x4 x, + 4×2-4×3-X4-0 x1 + 2×2-2×4 x1 + 2×2 -2×40 3 2 3
Expert Answer
Answer to a. Rewrite the system in matrix format, find the augmented matrix and reduce the augmented matrix to reduced row echelon… . . .
[Solved]Quit System Uirements Design Two Classes Solve Problem One Class Called Employee Stores Q37199221
 . Quit the system uirements . Design two classes to solve this problem. One class, called Employee, stores employee’s data; the other class, called EmployeeList, holds a list of employee objects (called a container). (Due by the end of lab 10) The class Employee should have the data members of id, first name, last name, rate, and hours. The following member functions should be provided: – a constructor to initialize employee’s data with id, first name, last name, rate and . hours. Use default arguments. A member function that sets the last name A member function that sets the first name A member function that sets the id A member function that sets the rate A member function that sets the hours A member function that retrieves the last name A member function that retrieves the first name A member function that retrieves the id A member function that retrieves the rate . – – – – . – A member function that retrieves the hours . A member function that computes and returns the wage. Show transcribed image text . Quit the system uirements . Design two classes to solve this problem. One class, called Employee, stores employee’s data; the other class, called EmployeeList, holds a list of employee objects (called a container). (Due by the end of lab 10) The class Employee should have the data members of id, first name, last name, rate, and hours. The following member functions should be provided: – a constructor to initialize employee’s data with id, first name, last name, rate and . hours. Use default arguments. A member function that sets the last name A member function that sets the first name A member function that sets the id A member function that sets the rate A member function that sets the hours A member function that retrieves the last name A member function that retrieves the first name A member function that retrieves the id A member function that retrieves the rate . – – – – . – A member function that retrieves the hours . A member function that computes and returns the wage.
. Quit the system uirements . Design two classes to solve this problem. One class, called Employee, stores employee’s data; the other class, called EmployeeList, holds a list of employee objects (called a container). (Due by the end of lab 10) The class Employee should have the data members of id, first name, last name, rate, and hours. The following member functions should be provided: – a constructor to initialize employee’s data with id, first name, last name, rate and . hours. Use default arguments. A member function that sets the last name A member function that sets the first name A member function that sets the id A member function that sets the rate A member function that sets the hours A member function that retrieves the last name A member function that retrieves the first name A member function that retrieves the id A member function that retrieves the rate . – – – – . – A member function that retrieves the hours . A member function that computes and returns the wage. Show transcribed image text . Quit the system uirements . Design two classes to solve this problem. One class, called Employee, stores employee’s data; the other class, called EmployeeList, holds a list of employee objects (called a container). (Due by the end of lab 10) The class Employee should have the data members of id, first name, last name, rate, and hours. The following member functions should be provided: – a constructor to initialize employee’s data with id, first name, last name, rate and . hours. Use default arguments. A member function that sets the last name A member function that sets the first name A member function that sets the id A member function that sets the rate A member function that sets the hours A member function that retrieves the last name A member function that retrieves the first name A member function that retrieves the id A member function that retrieves the rate . – – – – . – A member function that retrieves the hours . A member function that computes and returns the wage.
Expert Answer
Answer to . Quit the system uirements . Design two classes to solve this problem. One class, called Employee, stores employee’s da… . . .
[Solved]Show Stack Activation Record Instances Including Static Dynamic Chains Execution Reaches Q37173286

. Show the stack with all activation record instances, including static and dynamic chains, when execution reaches position 1 in the following skeletal program. The calling sequence for this program for execution to reach the subprogram subl is Main calls Subl Subl calls Sub2 Sub2 calls Sub3 ub3 calls Subl procedure Main is a, b : Float ;-Main’s local variable procedure Subl(f: Float) is b,cInteger:Subl’s local variable begin of Sub1 -Position 1 and – of Sub1 procedure Sub2 is b,c : Integer; –Sub2’s local variable procedur Sub3 is c : Float Sub3’s local variable begin -of Sub3 end – of Sub3 begin of Sub2 and – of Sub2 beginof Main and of Main 6. In Problem 5, suppose the last call to subl has finished and Sub3 is running. What is the (chain offset, local offset) pair for the reference to variable a, b and c? Show transcribed image text . Show the stack with all activation record instances, including static and dynamic chains, when execution reaches position 1 in the following skeletal program. The calling sequence for this program for execution to reach the subprogram subl is Main calls Subl Subl calls Sub2 Sub2 calls Sub3 ub3 calls Subl procedure Main is a, b : Float ;-Main’s local variable procedure Subl(f: Float) is b,cInteger:Subl’s local variable begin of Sub1 -Position 1 and – of Sub1 procedure Sub2 is b,c : Integer; –Sub2’s local variable procedur Sub3 is c : Float Sub3’s local variable begin -of Sub3 end – of Sub3 begin of Sub2 and – of Sub2 beginof Main and of Main 6. In Problem 5, suppose the last call to subl has finished and Sub3 is running. What is the (chain offset, local offset) pair for the reference to variable a, b and c?
Expert Answer
Answer to . Show the stack with all activation record instances, including static and dynamic chains, when execution reaches posit… . . .
[Solved]Tree N Distinct Elements Min Heap Binary Search Tree Must Look Like Justify Answer 5 Poin Q37189498

I. (a) A tree with n distinct elements is both a min-heap and a binary search tree. What must it look like? Justify your answer. [5 points] 1. (b) The textbook shows sorting methods primarily to arrays. Of the following sort algorithms, which are most appropriate to sort a Singly Linked List: insertion sort, merge sort, heap sort, or quick sort? Show examples to justify your answer. [S Show transcribed image text I. (a) A tree with n distinct elements is both a min-heap and a binary search tree. What must it look like? Justify your answer. [5 points] 1. (b) The textbook shows sorting methods primarily to arrays. Of the following sort algorithms, which are most appropriate to sort a Singly Linked List: insertion sort, merge sort, heap sort, or quick sort? Show examples to justify your answer. [S
Expert Answer
Answer to I. (a) A tree with n distinct elements is both a min-heap and a binary search tree. What must it look like? Justify your… . . .
[Solved]Solvewithhashing Java Problem 1 Given Array N Positive Numbers Give Algorithm Finding Fir Q37222819
- I. SolveWithHashing in java
Problem #1
Given an array of n positive numbers, give an algorithm forfinding the first element in the array which is repeated (may berepeated more than once). For example, in the array {0,3,2,1,2,2,3}the first repeated number is 3 (not 2). Utilize hashing where thekey is the element, and the valueis the position of the element in the array. Initially we store theposition of the element in the array as the value for this key. Ifwe get the same element again however, we just negate the currentvalue in the hash table. The negative value in the hash tableindicates that we have seen the same element more than once. Afterprocessing the complete input array, we scan the hash table withthe values iterator and return the highest negative indexed valuefrom it. The highest negative value indicates that we have seenthat element first among repeated elements.
Step1: You will utilize HashedDictionary classthat implements DictionaryInterface. Make yourself familiar withthe class implementation. Next, implement displayHashTable() methodin this class. SolveWithHashing class has testDisplayHashTablemethod you will use to test it.
Step2: Implement the algorithm ingetFirstRepeatedElement method. Note: the algorithm assumes thatrecorded positions are 1-based, for example the element at index 0has position 1.
Problem #2
Given two arrays a and b, and a numberk, consider the following algorithm for finding whetherthere exists a pair of elements, one of them from a andone from b, that add up to k.
- Select the set which has the smaller number of elements (swapthe reference variables if needed)
- For the selected set create a hash table (you can use theelement for the key and the value)
- Now scan the second array and check whether k-selectedelement exist in the hash table or not
- HINT look for a key that is computed as a delta between k andthe current element
- If it exists, then return the pair of elements
- Otherwise continue until we reach the end of the set.
IMPLEMENT CODE WHERE IT SAYS “TODO” import java.util.*;import java.util.NoSuchElementException;import java.io.Serializable; public class HashedDictionary<K,V> implements DictionaryInterface<K,V>,Serializable{ // The dictionary: private int numberOfEntries; private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 5; // Must be prime private static final int MAX_CAPACITY = 10000; // The hash table: private TableEntry<K, V>[] hashTable; private static final int MAX_SIZE = 2 * MAX_CAPACITY; private boolean initialized = false; private static final double MAX_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.5; // Fraction of hash table that can be filled private int probes; public HashedDictionary() { this(DEFAULT_CAPACITY); // Call next constructor } // end default constructor public HashedDictionary(int initialCapacity) { initialCapacity = checkCapacity(initialCapacity); this.numberOfEntries = 0; // Dictionary is empty // Set up hash table: // Initial size of hash table is same as initialCapacity if it is prime; // otherwise increase it until it is prime size int tableSize = getNextPrime(initialCapacity); checkSize(tableSize); // The cast is safe because the new array contains null entries @SuppressWarnings(“unchecked”) TableEntry<K, V>[] temp = (TableEntry<K, V>[])new TableEntry[tableSize]; this.hashTable = temp; this.initialized = true; this.probes = 0; } // end constructor // We’ve added this method to display the hash table for illustration and testing public void displayHashTable() { System.out.println(“The size of hash table is: ” + this.hashTable.length); System.out.println(“In displayHashTable – implement me”); // TODO Project1 #1 // displays “null” if there is no entry in the slot // displays “notIn” if an entry used to be there but was removed // displays the “KEY:” and its “VALUE:” if the entry is there System.out.println(); } // end display // Throws an exception if this object is not initialized. private void checkInitialization() { if (!this.initialized) throw new SecurityException (“HashedDictionary object is not initialized properly.”); } // end checkInitialization // Ensures that the client requests a capacity // that is not too small or too large. private int checkCapacity(int capacity) { if (capacity < DEFAULT_CAPACITY) capacity = DEFAULT_CAPACITY; else if (capacity > MAX_CAPACITY) throw new IllegalStateException(“Attempt to create a dictionary ” + “whose capacity is larger than ” + MAX_CAPACITY); return capacity; } // end checkCapacity // Throws an exception if the hash table becomes too large. private void checkSize(int size) { if (size > MAX_SIZE) throw new IllegalStateException(“Dictionary has become too large.”); } // end checkSize public int getNumberOfProbes() { return this.probes; } public V add(K key, V value) { checkInitialization(); if ((key == null) || (value == null)) throw new IllegalArgumentException(“Cannot add null to a dictionary.”); else { V oldValue; // Value to return int index = getHashIndex(key); index = probe(index, key); // Check for and resolve collision // Assertion: index is within legal range for hashTable assert (index >= 0) && (index < this.hashTable.length); if ( (this.hashTable[index] == null) || this.hashTable[index].isRemoved()) { // Key not found, so insert new entry this.hashTable[index] = new TableEntry<>(key, value); this.numberOfEntries++; oldValue = null; } else { // Key found; get old value for return and then replace it oldValue = this.hashTable[index].getValue(); this.hashTable[index].setValue(value); } // Ensure that hash table is large enough for another add if (isHashTableTooFull()) enlargeHashTable(); return oldValue; } } // end add public V remove(K key) { checkInitialization(); V removedValue = null; int index = getHashIndex(key); index = locate(index, key); if (index != -1) { // Key found; flag entry as removed and return its value removedValue = this.hashTable[index].getValue(); this.hashTable[index].setToRemoved(); this.numberOfEntries–; } // Else not found; result is null return removedValue; } // end remove public V getValue(K key) { checkInitialization(); V result = null; int index = getHashIndex(key); index = locate(index, key); if (index != -1) result = this.hashTable[index].getValue(); // Key found; get value // Else not found; result is null return result; } // end getValue public boolean contains(K key) { return getValue(key) != null; } // end contains public boolean isEmpty() { return this.numberOfEntries == 0; } // end isEmpty public int getSize() { return this.numberOfEntries; } // end getSize public final void clear() { checkInitialization(); for (int index = 0; index < this.hashTable.length; index++) hashTable[index] = null; this.numberOfEntries = 0; } // end clear public Iterator<K> getKeyIterator() { return new KeyIterator(); } // end getKeyIterator public Iterator<V> getValueIterator() { return new ValueIterator(); } // end getValueIterator private int getHashIndex(K key) { int hashIndex = key.hashCode() % this.hashTable.length; if (hashIndex < 0) { hashIndex = hashIndex + this.hashTable.length; } return hashIndex; } // end getHashIndex private int getHashIndexIncrement(K key) { // TODO Project 2 Part 2 int previousPrime = getPreviousPrime(this.hashTable.length); final int DEFAULT_PRIME = 7; int step = 0; System.out.println(“getHashIndexIncrement method – IMPLEMENT ME”); //System.out.println(“hash index increment is ” + step); return step; } // end getHashIndexIncrement // Precondition: checkInitialization has been called. private int probe(int index, K key) { // TODO Project 2 Part 2 boolean found = false; int removedStateIndex = -1; // Index of first location in removed state //int step = getHashIndexIncrement(key); // for double hashing ****** while ( !found && (this.hashTable[index] != null) ) { if (this.hashTable[index].isIn()) { if (key.equals(this.hashTable[index].getKey())) found = true; // Key found else { // Follow probe sequence index = (index + 1) % this.hashTable.length; // Linear probing this.probes++; } } else // Skip entries that were removed { // Save index of first location in removed state if (removedStateIndex == -1) removedStateIndex = index; index = (index + 1) % this.hashTable.length; // Linear probing this.probes++; } } // Assertion: Either key or null is found at hashTable[index] if (found || (removedStateIndex == -1) ) return index; // Index of either key or null else return removedStateIndex; // Index of an available location } // end probe // Precondition: checkInitialization has been called. private int locate(int index, K key) { // TODO Project 2 Part 2 boolean found = false; // int step = getHashIndexIncrement(key); // for double hashing ****** while ( !found && (this.hashTable[index] != null) ) { if ( this.hashTable[index].isIn() && key.equals(this.hashTable[index].getKey()) ) found = true; // Key found else { // Follow probe sequence index = (index + 1) % this.hashTable.length; // Linear probing ****** this.probes++; } } // Assertion: Either key or null is found at hashTable[index] int result = -1; if (found) result = index; return result; } // end locate
Expert Answer
Answer to I. SolveWithHashing in java Problem #1 Given an array of n positive numbers, give an algorithm for finding the first el… . . .
[Solved]True False 1init Method Called Whenever Set Data Attributes Given Object Using Setter Met Q37169529

I. True or False and Why 1.init method is called whenever you set the data attributes of a given object using the setter methods You cannot change the value of private data attribute outside the class using the getter method. 3. You have to add setter methods even when data attributes are declared as public. An accessor method of a class reads the value of the data member of the class and then returns its 4. value. 5. You can instantiate an object before creating a class template. 6. There is no need for setter and getter methods when data attributes are defined as public 7. Data hiding principle means that data attributes of a given object are not mutated and/or accessed directly through data attributes naming. 8. A getter method of a class changes the value of the data attribute (member) of the class. 9. The data attributes (members) of a class must be public. 10. The methods of a class designate actions to be executed by objects. Show transcribed image text I. True or False and Why 1.init method is called whenever you set the data attributes of a given object using the setter methods You cannot change the value of private data attribute outside the class using the getter method. 3. You have to add setter methods even when data attributes are declared as public. An accessor method of a class reads the value of the data member of the class and then returns its 4. value. 5. You can instantiate an object before creating a class template. 6. There is no need for setter and getter methods when data attributes are defined as public 7. Data hiding principle means that data attributes of a given object are not mutated and/or accessed directly through data attributes naming. 8. A getter method of a class changes the value of the data attribute (member) of the class. 9. The data attributes (members) of a class must be public. 10. The methods of a class designate actions to be executed by objects.
Expert Answer
Answer to I. True or False and Why 1.init method is called whenever you set the data attributes of a given object using the setter… . . .
[Solved]Typical Http Request Browser Web Server Might Contain Following Information Get People St Q37281213
 . (a) A typical HTTP request from a browser to a web server might contain the following information: GET /people/staff/iau/x.txt HTTP/1.1 Host: www.cs.kent.ac.uk User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) Chrome/56.0.2924.87 Accept: text/html:q 0.9.text/plain:q-0.8 Accept-Charset: ISO-8859-1,UTF-8;q=0.7,”;qs0.7 Accept-Language: fr,en:q-0.7,en-us:q 0.3 Referer: https://www.cs.kent.ac.uk/people/staff/iaulindex.html Explain in detail the meaning of the GET, Host and Referer lines. (C) [7 marks] (i) What part of the request can be used by a web server to identify the characteristics and capabilities of the requestor? How is such identification achieved, and what sort of capabilities are typically identified for requests from mobile devices? [10 marks] Show transcribed image text . (a) A typical HTTP request from a browser to a web server might contain the following information: GET /people/staff/iau/x.txt HTTP/1.1 Host: www.cs.kent.ac.uk User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) Chrome/56.0.2924.87 Accept: text/html:q 0.9.text/plain:q-0.8 Accept-Charset: ISO-8859-1,UTF-8;q=0.7,”;qs0.7 Accept-Language: fr,en:q-0.7,en-us:q 0.3 Referer: https://www.cs.kent.ac.uk/people/staff/iaulindex.html Explain in detail the meaning of the GET, Host and Referer lines. (C) [7 marks] (i) What part of the request can be used by a web server to identify the characteristics and capabilities of the requestor? How is such identification achieved, and what sort of capabilities are typically identified for requests from mobile devices? [10 marks]
. (a) A typical HTTP request from a browser to a web server might contain the following information: GET /people/staff/iau/x.txt HTTP/1.1 Host: www.cs.kent.ac.uk User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) Chrome/56.0.2924.87 Accept: text/html:q 0.9.text/plain:q-0.8 Accept-Charset: ISO-8859-1,UTF-8;q=0.7,”;qs0.7 Accept-Language: fr,en:q-0.7,en-us:q 0.3 Referer: https://www.cs.kent.ac.uk/people/staff/iaulindex.html Explain in detail the meaning of the GET, Host and Referer lines. (C) [7 marks] (i) What part of the request can be used by a web server to identify the characteristics and capabilities of the requestor? How is such identification achieved, and what sort of capabilities are typically identified for requests from mobile devices? [10 marks] Show transcribed image text . (a) A typical HTTP request from a browser to a web server might contain the following information: GET /people/staff/iau/x.txt HTTP/1.1 Host: www.cs.kent.ac.uk User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) Chrome/56.0.2924.87 Accept: text/html:q 0.9.text/plain:q-0.8 Accept-Charset: ISO-8859-1,UTF-8;q=0.7,”;qs0.7 Accept-Language: fr,en:q-0.7,en-us:q 0.3 Referer: https://www.cs.kent.ac.uk/people/staff/iaulindex.html Explain in detail the meaning of the GET, Host and Referer lines. (C) [7 marks] (i) What part of the request can be used by a web server to identify the characteristics and capabilities of the requestor? How is such identification achieved, and what sort of capabilities are typically identified for requests from mobile devices? [10 marks]
Expert Answer
Answer to . (a) A typical HTTP request from a browser to a web server might contain the following information: GET /people/staff/i… . . .
[Solved]Use Loop Structure Code Program Produces Following Output Take One Parameter User Let Spe Q37159460
hi i need help with the following questions:
thecode has too be in Rubyı. Use a loop structure and code a program that produces the following output (Take one parameter from the user to let them specify how many lines need to be printed): AAAB AAABA AAABAA AAABAAA AAABAAAB 2. Implement your own stack class (based on Array) with methods such as push, pop, length, and empty, and provide example test code that makes use of your stack class. 3. List 3 language design features of Ruby and evaluate them using short paragraphs (state both advantages and disadvantages). 4. (Extra Credit) Implement insertion sort algorithm. Read from the input file included in the assignment and write the sorted numbers into another file (sort in decreasing order and remove duplications). Show transcribed image text ı. Use a loop structure and code a program that produces the following output (Take one parameter from the user to let them specify how many lines need to be printed): AAAB AAABA AAABAA AAABAAA AAABAAAB 2. Implement your own stack class (based on Array) with methods such as push, pop, length, and empty, and provide example test code that makes use of your stack class. 3. List 3 language design features of Ruby and evaluate them using short paragraphs (state both advantages and disadvantages). 4. (Extra Credit) Implement insertion sort algorithm. Read from the input file included in the assignment and write the sorted numbers into another file (sort in decreasing order and remove duplications).
Expert Answer
Answer to ı. Use a loop structure and code a program that produces the following output (Take one parameter from the user to let … . . .
[Solved]Unload People Self Nunpeople Attempts Remove Nun People Bus Number People Supplied Larger Q37283356
python help please. Cannot import anything except math
* . unload people(self, nun_people)::Attempts to remove nun people from the bus. If the number of people supplied is larger than the number of people on the bus currently, return False and do not change the number of people currently on the bus. [You may imagine this as “the people are so confused by the request that they just stay where they are looking confused”] Classes Many of the methods required below are very regular- after youve seen one_init_method on this program, you’ve sort of seen them all. While there might be a bit more typing than usual, the amount of mental work to solve the puzzle” should be a bit minimal once you get used to the patterns. You will be writing four classes (Bus, Town, and Journey). Make sure you understand what these represent and how they relate to each other before continuing. Note and Assumptions: ‘ You can assume that num people is always a non-negative integer. This function should return True if the people were unloaded from the bus. Town class: Bus class: Instance variables Instance variables: # te nan, of thg town : stnng int int int string # the name of the bus # the naxínum number of people the bus can transport i the number of people currently on the bus # how fast the bus travels (in feet per second) loc x the town’s x location (in an x-y-coordinate system) # the town’s y location (in an x-y-coordinate system) # how long (in number of seconds) buss stop in this town :int max_people e nun people 1oc int stop tine . speed fps Methods: Methods: init (self, name, loc x, loc y, stop tine) constructor, initializes all instance variables. Assumption: All incoming arguments are good; there is no need to perform any checking. speed fps) :: constructor, initializes all instance variables, -init-(self, nun people should default to 0 when a bus is created with the constructor. max people, . nane, o o Assumptions: str(self) retus string representation with this fonmat (note, the quotes in the example are speed_fps and nax_people will always be a non-negative number name will be a non-empty string * just our string boundaries! The first character in this example string is N): Smithfield (e,3) Exchange tie:5.88 minutes” _str一(self) :: returns string representation with this format: Bus named GreyDog with S people will travel at 18.28mph o Notes: · The (03) in the example above are the coordinates of the town. Stop time is converted to number of minutes with 2 digits after the decimal point ” o Notes: ” The quotes in the example are just our string boundaries! The first character in the above example is B. This method reports nun _people (NOT max_people). ” . eq (self, other):: Override thecthod for Town objects; returns True or False. Cities should be “o each other if they are at the same kation (loc_x and loc_y), regardless of their name or stop time. For example, Town(“Smithfield”, 0, @, θ) and Town(“Snithy”, θ, θ, 10) would be the same since they are physically kocated in the same location. Bus speed is converted to mile per hour and always presented with 2 digits after the decimal point tine_to_travel (self, distance feet) travel distance_feet (distance in fect). Notes and Assumptions Returns how long (in whole seconds) this bus wl ake to distance_to_toun(self, town) Returns the distance between two towns (based on their x and y locations) as a loat (no truncating). Remember ab-c! o This always returns an integer – you could use integer division () or normal division followed by int) conversion to truncate the fractional part. You can assume that distance feet is always a non-negative integer. ourney class: Instance variables bus load_people(self, num_people) Attempts to put num_people onto the bus and update nun_people. If the number of people supplied would not fit on the bus, return False and do not change the number of pcople currently on the bus. [You may imagine this as “the pcople get into a fight and no one is allowed on the bus”.] :Bus # the bus r king the journey V the towns the bus will visit, in order # the time the bus will begin its journey # (in seconds since January 1st, 1970) list of Town objects int e destinations start tine Note and Assumptions: o You can assume that nun people is always a non-negative integer This function should return True if the people were loaded on the bus. Note: Why Thursday, Jan. Ist 1970? See: Show transcribed image text * . unload people(self, nun_people)::Attempts to remove nun people from the bus. If the number of people supplied is larger than the number of people on the bus currently, return False and do not change the number of people currently on the bus. [You may imagine this as “the people are so confused by the request that they just stay where they are looking confused”] Classes Many of the methods required below are very regular- after youve seen one_init_method on this program, you’ve sort of seen them all. While there might be a bit more typing than usual, the amount of mental work to solve the puzzle” should be a bit minimal once you get used to the patterns. You will be writing four classes (Bus, Town, and Journey). Make sure you understand what these represent and how they relate to each other before continuing. Note and Assumptions: ‘ You can assume that num people is always a non-negative integer. This function should return True if the people were unloaded from the bus. Town class: Bus class: Instance variables Instance variables: # te nan, of thg town : stnng int int int string # the name of the bus # the naxínum number of people the bus can transport i the number of people currently on the bus # how fast the bus travels (in feet per second) loc x the town’s x location (in an x-y-coordinate system) # the town’s y location (in an x-y-coordinate system) # how long (in number of seconds) buss stop in this town :int max_people e nun people 1oc int stop tine . speed fps Methods: Methods: init (self, name, loc x, loc y, stop tine) constructor, initializes all instance variables. Assumption: All incoming arguments are good; there is no need to perform any checking. speed fps) :: constructor, initializes all instance variables, -init-(self, nun people should default to 0 when a bus is created with the constructor. max people, . nane, o o Assumptions: str(self) retus string representation with this fonmat (note, the quotes in the example are speed_fps and nax_people will always be a non-negative number name will be a non-empty string * just our string boundaries! The first character in this example string is N): Smithfield (e,3) Exchange tie:5.88 minutes” _str一(self) :: returns string representation with this format: Bus named GreyDog with S people will travel at 18.28mph o Notes: · The (03) in the example above are the coordinates of the town. Stop time is converted to number of minutes with 2 digits after the decimal point ” o Notes: ” The quotes in the example are just our string boundaries! The first character in the above example is B. This method reports nun _people (NOT max_people). ” . eq (self, other):: Override thecthod for Town objects; returns True or False. Cities should be “o each other if they are at the same kation (loc_x and loc_y), regardless of their name or stop time. For example, Town(“Smithfield”, 0, @, θ) and Town(“Snithy”, θ, θ, 10) would be the same since they are physically kocated in the same location. Bus speed is converted to mile per hour and always presented with 2 digits after the decimal point tine_to_travel (self, distance feet) travel distance_feet (distance in fect). Notes and Assumptions Returns how long (in whole seconds) this bus wl ake to distance_to_toun(self, town) Returns the distance between two towns (based on their x and y locations) as a loat (no truncating). Remember ab-c! o This always returns an integer – you could use integer division () or normal division followed by int) conversion to truncate the fractional part. You can assume that distance feet is always a non-negative integer. ourney class: Instance variables bus load_people(self, num_people) Attempts to put num_people onto the bus and update nun_people. If the number of people supplied would not fit on the bus, return False and do not change the number of pcople currently on the bus. [You may imagine this as “the pcople get into a fight and no one is allowed on the bus”.] :Bus # the bus r king the journey V the towns the bus will visit, in order # the time the bus will begin its journey # (in seconds since January 1st, 1970) list of Town objects int e destinations start tine Note and Assumptions: o You can assume that nun people is always a non-negative integer This function should return True if the people were loaded on the bus. Note: Why Thursday, Jan. Ist 1970? See:
Expert Answer
Answer to * . unload people(self, nun_people)::Attempts to remove nun people from the bus. If the number of people supplied is lar… . . .

