[Solved]1 Using Std Repeat Instruction Ensures Characters Read 2 Order Repeat Zf Clear Use 3 Execu Q37182711
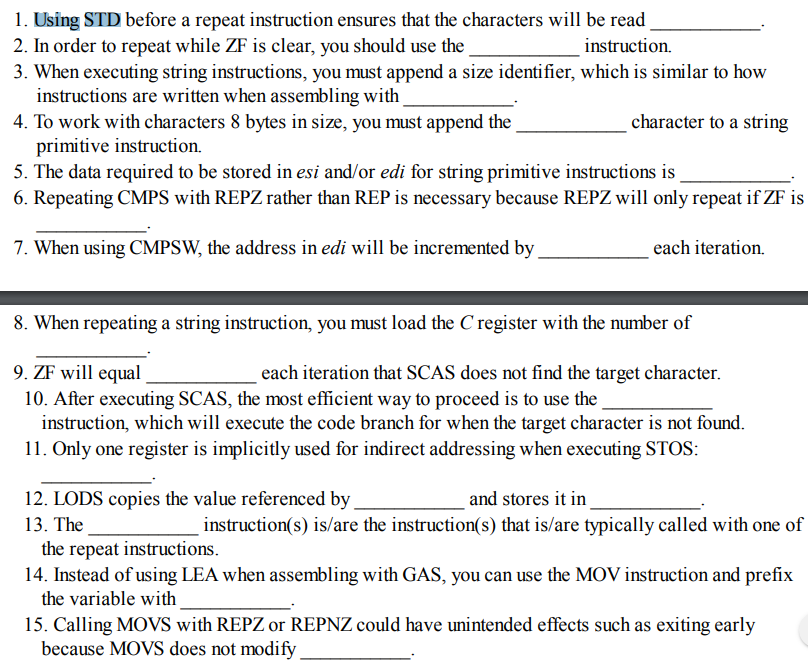
1. Using STD before a repeat instruction ensures that the characters will be read 2. In order to repeat while ZF is clear, you should use the 3. When executing string instructions, you must append a size identifier, which is similar to how instruction. instructions are written when assembling with 4. To work with characters 8 bytes in size, you must append the character to a string primitive instruction. 5. The data required to be stored in esi and/or edi for string primitive instructions is 6. Repeating CMPS with REPZ rather than REP is necessary because REPZ will only repeat if ZF is 7. When using CMPSW, the address in edi wil be incremented by each iteration. 8. When repeating a string instruction, you must load the C register with the number of each iteration that SCAS does not find the target character. 9. ZF will equal 10. After executing SCAS, the most efficient way to proceed is to use the instruction, which will execute the code branch for when the target character is not found. 11. Only one register is implicitly used for indirect addressing when executing STOS: 12. LODS copies the value referenced by and stores it in instruction(s) is/are the instruction(s) that is/are typically called with one of 13. The 14. Instead of using LEA when assembling with GAS, you can use the MOV instruction and prefix 15. Calling MOVS with REPZ or REPNZ could have unintended effects such as exiting early the repeat instructions. the variable with because MOVS does not modify Show transcribed image text 1. Using STD before a repeat instruction ensures that the characters will be read 2. In order to repeat while ZF is clear, you should use the 3. When executing string instructions, you must append a size identifier, which is similar to how instruction. instructions are written when assembling with 4. To work with characters 8 bytes in size, you must append the character to a string primitive instruction. 5. The data required to be stored in esi and/or edi for string primitive instructions is 6. Repeating CMPS with REPZ rather than REP is necessary because REPZ will only repeat if ZF is 7. When using CMPSW, the address in edi wil be incremented by each iteration. 8. When repeating a string instruction, you must load the C register with the number of each iteration that SCAS does not find the target character. 9. ZF will equal 10. After executing SCAS, the most efficient way to proceed is to use the instruction, which will execute the code branch for when the target character is not found. 11. Only one register is implicitly used for indirect addressing when executing STOS: 12. LODS copies the value referenced by and stores it in instruction(s) is/are the instruction(s) that is/are typically called with one of 13. The 14. Instead of using LEA when assembling with GAS, you can use the MOV instruction and prefix 15. Calling MOVS with REPZ or REPNZ could have unintended effects such as exiting early the repeat instructions. the variable with because MOVS does not modify
Expert Answer
Answer to 1. Using STD before a repeat instruction ensures that the characters will be read 2. In order to repeat while ZF is clea… . . .
OR

