[solved]-Code Already Provided Define Function Named Vectorfun Accepts Two Input Variables B Descri Q38992956
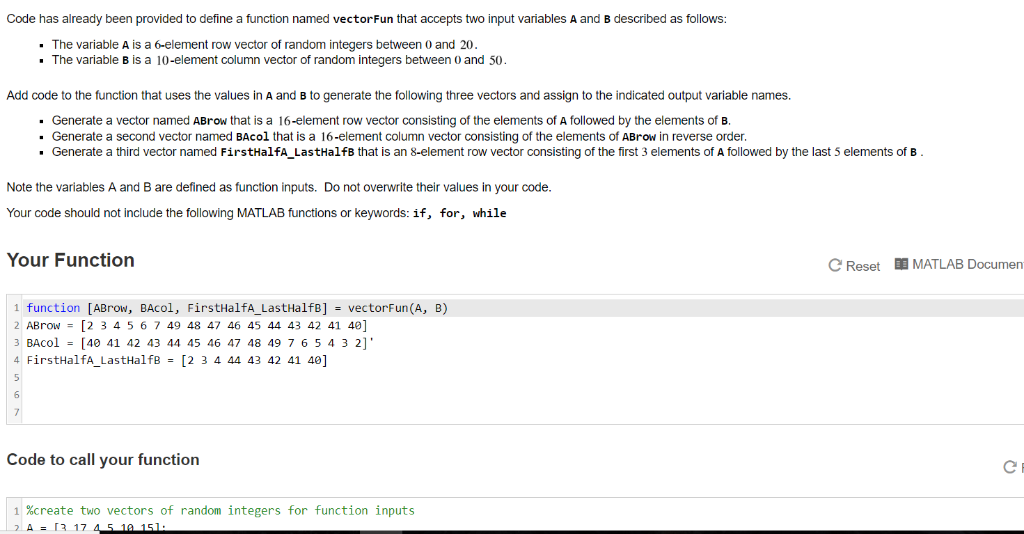

Code has already been provided to define a function named vectorFun that accepts two input variables A and B described as follows: . The variable A is a 6-element row vector of random integers between 0 and 20. • The variable B is a 10-element column vector of random integers between 0 and 50. Add code to the function that uses the values in A and B to generate the following three vectors and assign to the indicated output variable names. . Generate a vector named ABrow that is a 16-element row vector consisting of the elements of A followed by the elements of B. . Generate a second vector named Bacol that is a 16-element column vector consisting of the elements of ABrow in reverse order. • Generate a third vector named FirstHalfA_LastHalfB that is an 8-element row vector consisting of the first 3 elements of A followed by the last 5 elements of B. Note the variables A and B are defined as function inputs. Do not overwrite their values in your code. Your code should not include the following MATLAB functions or keywords: if, for, while Your Function C Reset MATLAB Document 1 function [ABrow, Bacol, FirstHalfA_LastHalfB] = vectorFun(A, B) 2 ABrow = [2 3 4 5 6 7 49 48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40] 3 Bacol = [40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 7 6 5 4 3 2]’ 4 FirstHalfA_LastHalfB = [2 3 4 44 43 42 41 40] Code to call your function 1 %create two vectors of random integers for function inputs 2. A = [3 17 4 5 10 151 Code has already been provided to define a function named vector fun that accepts a scalar integer value as input and assigns it to the variable A. Add commands to do the following operations and 1. Generate a row vector that consists of even integers starting at 0 and ending at twice the value of A with increments of 2. Assign this vector to the output variable Up. 2. Generate a second output variable that is a vector named UpDown that consists of the elements in Up followed by odd integers counting down from (2A – 1) to 1. For example, if A = 5, then the expected outputs are: Up – [ 2 4 6 8 10] and UpDown = [0 2 4 6 8 10 9 7 5 3 1] Solve this problem using vectorized code (i.e. do not use a loop in your solution.) Note the variable A is defined as a function input. Do not overwrite the value in your code. Your Function C Reset MATLAB Documentation i function [Up, UpDown] – vector Fun(A) 2 %Enter the commands for your function here. Be sure to assign values 3 %to each of the output variables defined in the function command on line 1. Code to call your function C Reset 1 [up, UpDown] = vectorFun(5); Consider the Leibniz series: Write a script to generate a vector of the first twenty terms of this series. Assign the vector of series terms to a row vector variable named LeibnizTerms. Solve this problem using vectorized code (i.e. do not use a loop in your solution.) Your Script C Reset MATLAB Documentation Run Script Consider the Leibniz series: Code has already been provided to define a function named leibnizSummation that accepts a single scalar input N and defines the output variable sumterms. Add code that computes the summation leibnizSummation. Solve this problem using vectorized code (i.e. do not use a loop in your solution). Note the variable N is defined as a function input. Do not overwrite the value in your code. Your Function C Reset MATLAB Documentation 1 function sumTerms = leibnizSummation (N) 2 %Enter the commands for your function here. Be sure to assign a value 3 %to the output variable sumTerms defined in the function command on line 1. Code to call your function C Reset 1 SumTerms = leibniz Summation(6); The pressure, volume, temperature, and mass of an ideal gas are related by the ideal gas equation of state: PV = MRT where P represents pressure (Pascals), V represents volume (cubic meters), m represents mass (grams), T represents temperature (Kelvin), and Mrepresents the molecular mass of the gas (grams/mc The temperature decrease a gas experiences during a cooling process depends on the molecular weight, M, of the gas. Consider the following two gasses: • Oxygen, O2, M = 15.999 grams/mole · Carbon Dioxide, CO2, M = 44.01 grams/mole Suppose a mass of 100 grams of gas at a starting pressure of 500 x 109 Pascals undergoes a cooling process at a constant volume of V = 0.15 cubic meters. Heat is removed until the pressure decr Write a script to compute the temperature values corresponding to 100 equally spaced pressure values in descending order ranging from 500 x 109 Pascals to 100 x 109 Pascals for each of the two ga named TO2. Assign the temperature values for carbon dioxide as a column vector to a variable named TCO2. Solve this problem using vectorized code (.e. do not use a loop in your solution.) Your Script Reset MATLAB Documentation Consider the motion of an object modeled with ideal projectile motion (neglecting air resistance), The trajectory of the object can be derived from basic physics and is given by the formula: y = xtan y = xtan -1 X’ 2 (cos() 82 + yo where y is the height x is the horizontal distance in meters, o is the initial angle, g is the acceleration due to gravity (g = 9.81m/s2), Vo is the initial velocity in m/s, and yo is the initial height in meters. Tt using the formula: (v sin 0 + V (sin )2 + 2gyo). d = Locos Write a script to calculate the following three trajectories: • Trajectory1: 0 = 30°, Vo = 25 m/s, yo = 3.5 m • Trajectory2: 0,= 45, 10 = 25 m/s, yo = 3.5 m • Trajectory3: 63 = 60°, Vo = 25 m/s, yo = 3.5 m For each value of e, generate a column vector of 200 evenly-spaced x values starting at 0 and ending at the range d. Compute the associated column vectors of y values and assign the results to the Use the plot command to generate a figure with a plot of all three trajectories on a single set of axes. Use MATLAB commands to add an appropriate title, axis labels, grid and legend to the figure. ENGR 240 Summer 2019 > PA1 > P9. Arrhenius Equation (semilog plot) O solutions submitted (max: Unlimited) The Arrhenius equation models the temperature dependence of a chemical reaction rate. The formula is most commonly written as k= tema where k is the rate constant in units of inverse seconds, 7 is the temperature in units of Kelvin, A is the pre-exponential factor that is a constant for a specific chemical reaction, E. is the activation ener constant and has a value of 8.31447 Joules/(mole-Kelvin). Note the e in the formula is the exponential function. Consider a reaction in which E. = 1.11 x 10 Joules/mole and A = 2.126 10° inverse seconds. Write a script to compute values of k for temperatures ranging from 250 Kelvin to 400 Kelvin in incren Assign the k values to a column vector variable reactionRate. Next use the semilogy command to generate a properly-labeled graph of k versus T using a logarithmic axis for k (the y-axis). Use MATLAB commands to add an appropriate title, axis labels, grid and Solve this problem using vectorized code (i.e. do not use a loop in your solution.) Your Script C Reset MATLAB Documentation Show transcribed image text Code has already been provided to define a function named vectorFun that accepts two input variables A and B described as follows: . The variable A is a 6-element row vector of random integers between 0 and 20. • The variable B is a 10-element column vector of random integers between 0 and 50. Add code to the function that uses the values in A and B to generate the following three vectors and assign to the indicated output variable names. . Generate a vector named ABrow that is a 16-element row vector consisting of the elements of A followed by the elements of B. . Generate a second vector named Bacol that is a 16-element column vector consisting of the elements of ABrow in reverse order. • Generate a third vector named FirstHalfA_LastHalfB that is an 8-element row vector consisting of the first 3 elements of A followed by the last 5 elements of B. Note the variables A and B are defined as function inputs. Do not overwrite their values in your code. Your code should not include the following MATLAB functions or keywords: if, for, while Your Function C Reset MATLAB Document 1 function [ABrow, Bacol, FirstHalfA_LastHalfB] = vectorFun(A, B) 2 ABrow = [2 3 4 5 6 7 49 48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40] 3 Bacol = [40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 7 6 5 4 3 2]’ 4 FirstHalfA_LastHalfB = [2 3 4 44 43 42 41 40] Code to call your function 1 %create two vectors of random integers for function inputs 2. A = [3 17 4 5 10 151
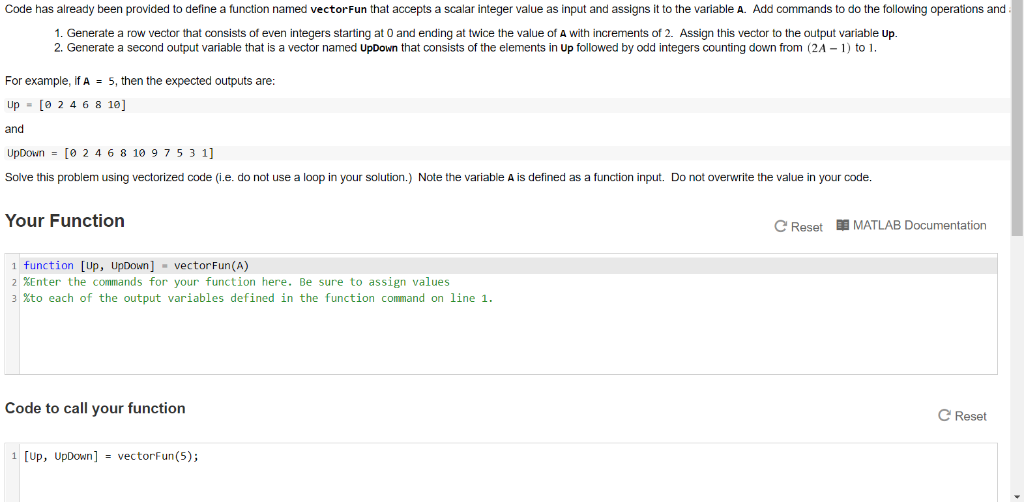
Code has already been provided to define a function named vector fun that accepts a scalar integer value as input and assigns it to the variable A. Add commands to do the following operations and 1. Generate a row vector that consists of even integers starting at 0 and ending at twice the value of A with increments of 2. Assign this vector to the output variable Up. 2. Generate a second output variable that is a vector named UpDown that consists of the elements in Up followed by odd integers counting down from (2A – 1) to 1. For example, if A = 5, then the expected outputs are: Up – [ 2 4 6 8 10] and UpDown = [0 2 4 6 8 10 9 7 5 3 1] Solve this problem using vectorized code (i.e. do not use a loop in your solution.) Note the variable A is defined as a function input. Do not overwrite the value in your code. Your Function C Reset MATLAB Documentation i function [Up, UpDown] – vector Fun(A) 2 %Enter the commands for your function here. Be sure to assign values 3 %to each of the output variables defined in the function command on line 1. Code to call your function C Reset 1 [up, UpDown] = vectorFun(5);
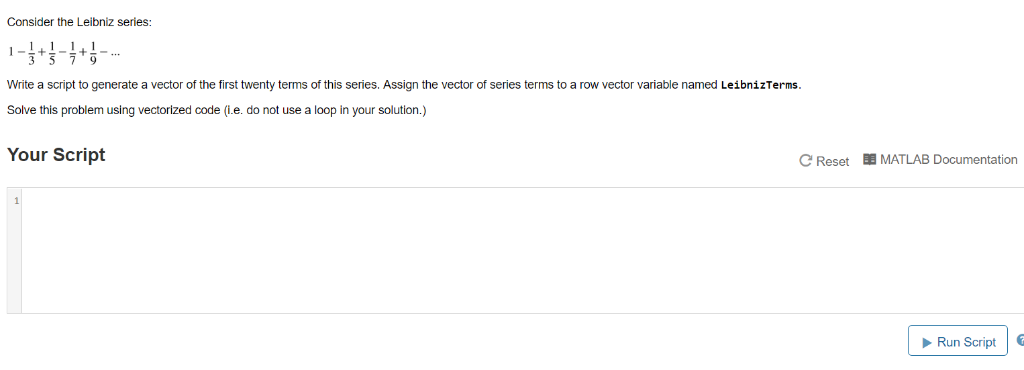
Consider the Leibniz series: Write a script to generate a vector of the first twenty terms of this series. Assign the vector of series terms to a row vector variable named LeibnizTerms. Solve this problem using vectorized code (i.e. do not use a loop in your solution.) Your Script C Reset MATLAB Documentation Run Script
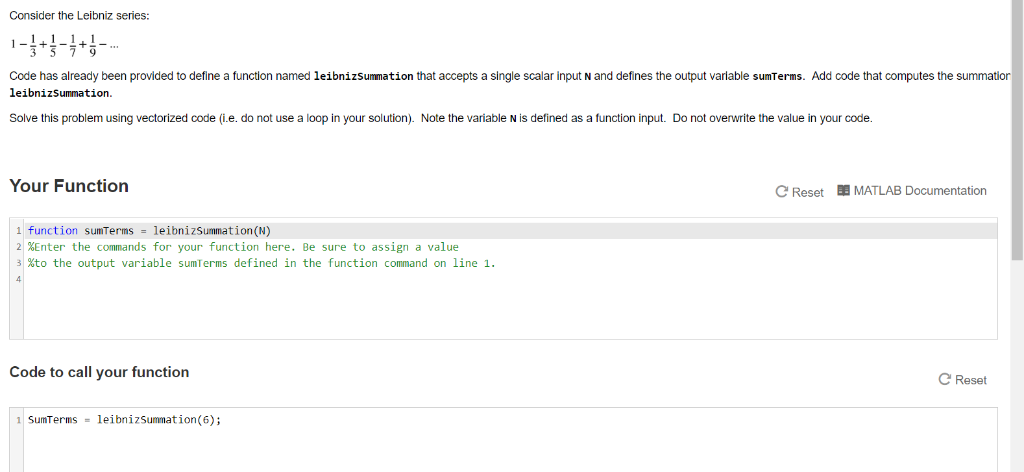
Consider the Leibniz series: Code has already been provided to define a function named leibnizSummation that accepts a single scalar input N and defines the output variable sumterms. Add code that computes the summation leibnizSummation. Solve this problem using vectorized code (i.e. do not use a loop in your solution). Note the variable N is defined as a function input. Do not overwrite the value in your code. Your Function C Reset MATLAB Documentation 1 function sumTerms = leibnizSummation (N) 2 %Enter the commands for your function here. Be sure to assign a value 3 %to the output variable sumTerms defined in the function command on line 1. Code to call your function C Reset 1 SumTerms = leibniz Summation(6);
The pressure, volume, temperature, and mass of an ideal gas are related by the ideal gas equation of state: PV = MRT where P represents pressure (Pascals), V represents volume (cubic meters), m represents mass (grams), T represents temperature (Kelvin), and Mrepresents the molecular mass of the gas (grams/mc The temperature decrease a gas experiences during a cooling process depends on the molecular weight, M, of the gas. Consider the following two gasses: • Oxygen, O2, M = 15.999 grams/mole · Carbon Dioxide, CO2, M = 44.01 grams/mole Suppose a mass of 100 grams of gas at a starting pressure of 500 x 109 Pascals undergoes a cooling process at a constant volume of V = 0.15 cubic meters. Heat is removed until the pressure decr Write a script to compute the temperature values corresponding to 100 equally spaced pressure values in descending order ranging from 500 x 109 Pascals to 100 x 109 Pascals for each of the two ga named TO2. Assign the temperature values for carbon dioxide as a column vector to a variable named TCO2. Solve this problem using vectorized code (.e. do not use a loop in your solution.) Your Script Reset MATLAB Documentation
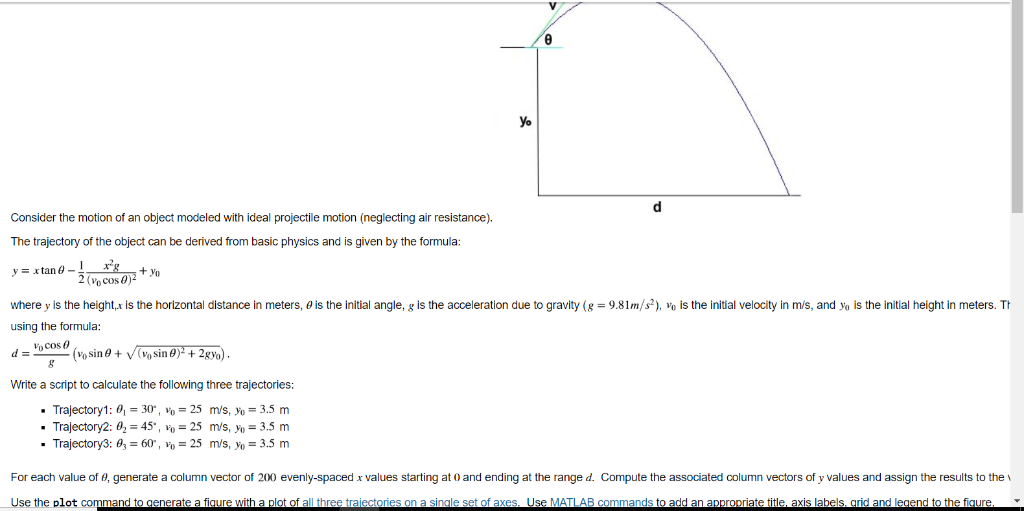
Consider the motion of an object modeled with ideal projectile motion (neglecting air resistance), The trajectory of the object can be derived from basic physics and is given by the formula: y = xtan y = xtan -1 X’ 2 (cos() 82 + yo where y is the height x is the horizontal distance in meters, o is the initial angle, g is the acceleration due to gravity (g = 9.81m/s2), Vo is the initial velocity in m/s, and yo is the initial height in meters. Tt using the formula: (v sin 0 + V (sin )2 + 2gyo). d = Locos Write a script to calculate the following three trajectories: • Trajectory1: 0 = 30°, Vo = 25 m/s, yo = 3.5 m • Trajectory2: 0,= 45, 10 = 25 m/s, yo = 3.5 m • Trajectory3: 63 = 60°, Vo = 25 m/s, yo = 3.5 m For each value of e, generate a column vector of 200 evenly-spaced x values starting at 0 and ending at the range d. Compute the associated column vectors of y values and assign the results to the Use the plot command to generate a figure with a plot of all three trajectories on a single set of axes. Use MATLAB commands to add an appropriate title, axis labels, grid and legend to the figure.
ENGR 240 Summer 2019 > PA1 > P9. Arrhenius Equation (semilog plot) O solutions submitted (max: Unlimited) The Arrhenius equation models the temperature dependence of a chemical reaction rate. The formula is most commonly written as k= tema where k is the rate constant in units of inverse seconds, 7 is the temperature in units of Kelvin, A is the pre-exponential factor that is a constant for a specific chemical reaction, E. is the activation ener constant and has a value of 8.31447 Joules/(mole-Kelvin). Note the e in the formula is the exponential function. Consider a reaction in which E. = 1.11 x 10 Joules/mole and A = 2.126 10° inverse seconds. Write a script to compute values of k for temperatures ranging from 250 Kelvin to 400 Kelvin in incren Assign the k values to a column vector variable reactionRate. Next use the semilogy command to generate a properly-labeled graph of k versus T using a logarithmic axis for k (the y-axis). Use MATLAB commands to add an appropriate title, axis labels, grid and Solve this problem using vectorized code (i.e. do not use a loop in your solution.) Your Script C Reset MATLAB Documentation
Expert Answer
Answer to Code has already been provided to define a function named vectorFun that accepts two input variables A and B described a… . . .
OR

